Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is the process of exchanging one currency for another in a global market that operates 24 hours a day. As the largest financial market in the world, the forex market offers vast opportunities for traders. This tutorial aims to provide a comprehensive overview of forex trading, covering everything from basic concepts to strategies and risk management.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Forex Trading
- What is Forex?
- How the Forex Market Works
- Currency Pairs
- Major, Minor, and Exotic Pairs
- Understanding Bid and Ask Prices
- How to Start Trading Forex
- Choosing a Forex Broker
- Setting Up a Trading Account
- Using Trading Platforms
- Understanding Forex Quotes
- Pips, Spreads, and Leverage
- Margin and Margin Call
- Basic Trading Strategies
- Technical Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis
- Risk Management in Forex Trading
- Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders
- Position Sizing
- Psychology of Trading
- Emotional Discipline
- Common Trading Mistakes
- Conclusion and Next Steps
1. Introduction to Forex Trading
What is Forex?
Forex, short for foreign exchange, refers to the global marketplace where currencies are traded. Unlike stocks, forex trading doesn’t take place on centralized exchanges; instead, it operates over-the-counter (OTC) through a network of banks, brokers, and financial institutions.
How the Forex Market Works
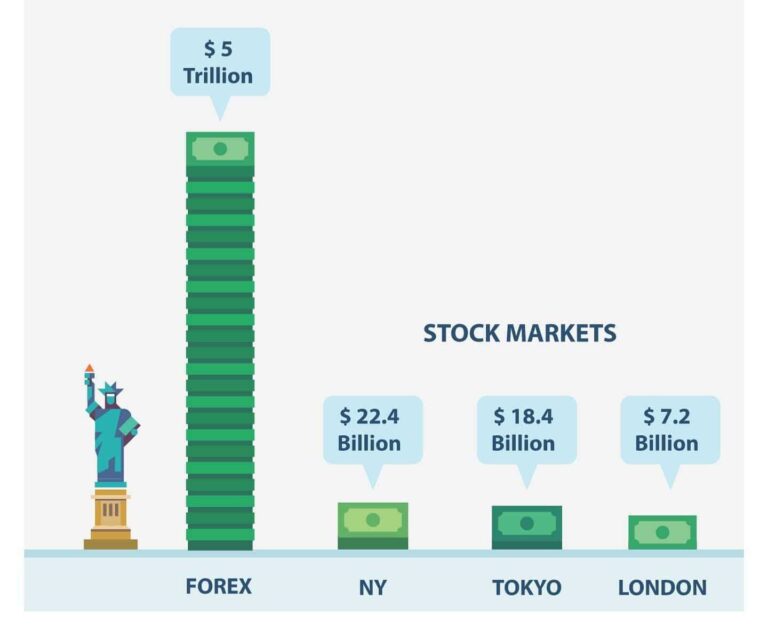
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, with trading sessions overlapping across major financial centers such as London, New York, and Tokyo. Currencies are traded in pairs, meaning when you buy one currency, you simultaneously sell another. The value of a currency pair fluctuates based on various factors, including economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events.
2. Currency Pairs
Major, Minor, and Exotic Pairs
Currency pairs are categorized into three types:
- Major Pairs: These include the most traded currencies in the world, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD.
- Minor Pairs: These are less commonly traded and do not include the US dollar, like EUR/GBP or AUD/NZD.
- Exotic Pairs: These involve a major currency and a currency from a developing economy, such as USD/TRY (Turkish Lira) or EUR/SEK (Swedish Krona).
Understanding Bid and Ask Prices
In forex trading, each currency pair has two prices:
- Bid Price: The price at which you can sell the base currency.
- Ask Price: The price at which you can buy the base currency.
The difference between the bid and ask price is known as the spread, which is the broker’s profit for facilitating the trade.
3. How to Start Trading Forex
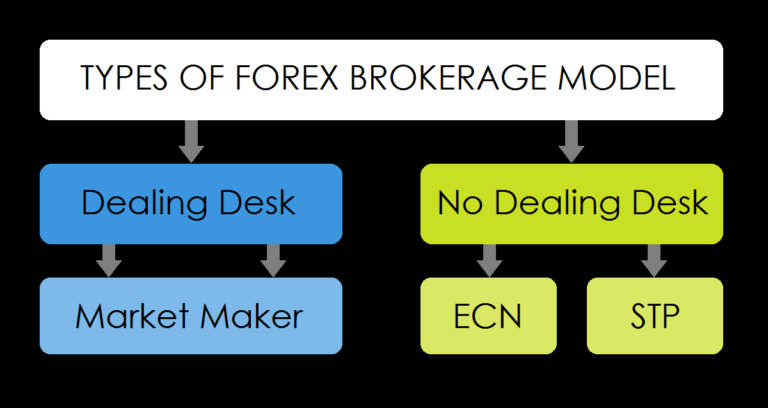
Choosing a Forex Broker
Selecting a reputable forex broker is crucial for your trading success. Consider the following factors:
- Regulation: Ensure the broker is regulated by a recognized authority (e.g., FCA, NFA).
- Trading Costs: Compare spreads, commissions, and overnight fees.
- Trading Platforms: Look for user-friendly platforms that offer the necessary tools for analysis.
Setting Up a Trading Account
Once you choose a broker, you need to open a trading account. This typically involves:
- Filling out an application form.
- Providing identification (like a passport or driver’s license).
- Making an initial deposit (check minimum deposit requirements).
Using Trading Platforms
Most brokers offer trading platforms such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5). These platforms allow you to execute trades, analyze the market, and manage your account. Familiarize yourself with the platform’s features, including charting tools, indicators, and order types.
4. Understanding Forex Quotes
Pips, Spreads, and Leverage
- Pips: A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price move that a currency pair can make. For most pairs, it is the fourth decimal place (e.g., 1.2345 to 1.2346).
- Spread: The difference between the bid and ask price. A smaller spread usually indicates a more favorable trading condition.
- Leverage: Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. For example, with 100:1 leverage, you can control a $10,000 position with just $100. While leverage can amplify gains, it can also amplify losses.
Margin and Margin Call
Margin is the amount of capital required to open a leveraged position. If your account balance falls below the required margin level, you may receive a margin call, requiring you to deposit more funds or close some positions.
5. Basic Trading Strategies
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price movements using charts and indicators. Common tools include:
- Moving Averages: Help smooth out price action and identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Key price levels where the market tends to reverse or consolidate.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis looks at economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events to assess currency value. Key reports to watch include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Employment Data
- Central Bank Decisions
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis gauges the market’s mood. Tools like the Commitment of Traders (COT) report can provide insights into whether traders are bullish or bearish on a currency.
6. Risk Management in Forex Trading
Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders
- Stop Loss: An order to close a trade at a specified price to limit losses. This is crucial in volatile markets.
- Take Profit: An order to close a trade at a specified profit level, ensuring you secure gains before the market reverses.
Position Sizing
Proper position sizing helps manage risk. A common rule is to risk only 1-2% of your trading capital on a single trade. This approach can help protect your account from significant losses.
7. Psychology of Trading
Emotional Discipline
Trading can evoke strong emotions, such as fear and greed. Maintaining emotional discipline is essential for long-term success. Here are some tips:
- Stick to Your Plan: Develop a trading plan and follow it consistently.
- Avoid Revenge Trading: Don’t try to recover losses immediately; it often leads to poor decisions.
Common Trading Mistakes
- Overleveraging: Using too much leverage can quickly lead to significant losses.
- Ignoring Risk Management: Failing to set stop-loss orders can result in catastrophic losses.
- Chasing Losses: Trying to recover losses with impulsive trades can lead to further losses.
8. Conclusion and Next Steps
Forex trading offers exciting opportunities, but it requires dedication, knowledge, and discipline. To get started:
- Educate Yourself: Continue learning about trading strategies, market analysis, and risk management.
- Practice on a Demo Account: Many brokers offer demo accounts that allow you to practice trading with virtual funds.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Outline your trading goals, strategies, and risk management rules.
As you gain experience, refine your approach, and adapt to changing market conditions. Remember, successful trading is a marathon, not a sprint.
By following this guide, you should now have a solid foundation in forex trading. Always stay curious, keep learning, and be prepared for the challenges that lie ahead in your trading journey. Happy trading!