Introduction
Stock trading can seem overwhelming for beginners, but it’s one of the most effective ways to build wealth over time. Whether you want to generate passive income or actively manage your portfolio, understanding how the stock market works is essential. This guide will break down the key aspects of stock trading, helping you make informed decisions as you begin your trading journey.
In this comprehensive 2500-word guide, we’ll cover:
- What is Stock Trading?
- How the Stock Market Works
- Types of Stock Trading
- Basic Terms and Concepts Every Beginner Should Know
- How to Start Trading Stocks
- Popular Trading Strategies for Beginners
- Tips for Managing Risk
- Best Platforms for Beginners
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Final Thoughts and Next Steps
1. What is Stock Trading?
Stock trading refers to the buying and selling of shares in a company. When you buy a stock, you are purchasing a small piece of ownership in that company, known as a “share.” Traders aim to profit by buying stocks at a lower price and selling them at a higher price.
Stock trading differs from long-term investing in that traders focus on shorter time frames, trying to capitalize on market fluctuations. Long-term investors, on the other hand, typically hold onto stocks for years or even decades, focusing on overall growth.
2. How the Stock Market Works
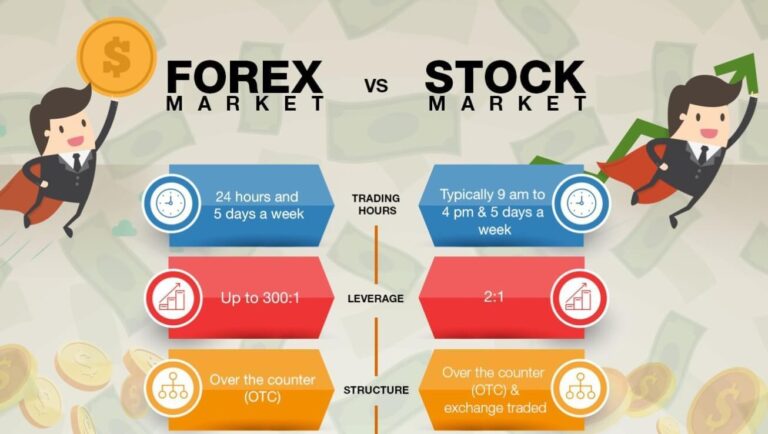
The stock market is a marketplace where investors buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. The most well-known exchanges in the United States are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. These exchanges function as intermediaries, facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
Stocks are listed on these exchanges, and their prices fluctuate based on demand and supply. If more people want to buy a stock, the price rises. If more people want to sell a stock, the price falls.
- Stock Tickers: Each company listed on an exchange has a unique ticker symbol. For example, Apple’s ticker is AAPL, while Google’s parent company, Alphabet, trades under GOOGL.
3. Types of Stock Trading
There are several ways to approach stock trading, each requiring different levels of expertise and risk tolerance. Let’s look at the primary types of trading:
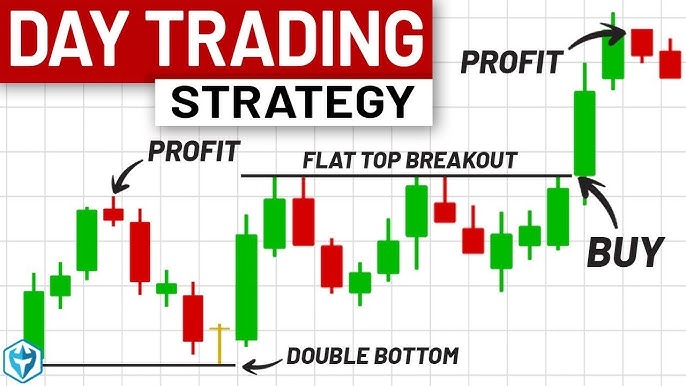
a) Day Trading
Day traders buy and sell stocks within a single day. The goal is to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations, often using technical analysis and charts to make quick decisions. Day trading is fast-paced and high-risk but can also be profitable for experienced traders.
b) Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding stocks for a few days or weeks to take advantage of price “swings.” Swing traders use both technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential entry and exit points. It is slower-paced than day trading but still requires active monitoring.
c) Position Trading
Position traders hold stocks for several months or years, focusing on the long-term trends and performance of a company. This strategy is ideal for those who want a middle ground between day trading and long-term investing.
d) Scalping
Scalping is a very short-term trading strategy where traders make multiple small trades in seconds or minutes, aiming to make quick profits from tiny price movements. It’s high-risk and requires advanced market knowledge and fast reflexes.
4. Basic Terms and Concepts Every Beginner Should Know
Understanding basic stock market terminology is crucial for beginners. Here are some essential terms:
a) Ask and Bid Price
- Ask Price: The lowest price at which a seller is willing to sell a stock.
- Bid Price: The highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a stock.
The difference between these two prices is called the spread.
b) Market Order vs. Limit Order
- Market Order: A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a stock immediately at the best available current price.
- Limit Order: A limit order sets a specific price at which a stock should be bought or sold. The trade will only execute if the stock reaches that price.
c) Bull Market vs. Bear Market
- Bull Market: A market characterized by rising stock prices. Traders are optimistic about future growth.
- Bear Market: A market in decline, where stock prices fall and investors are generally pessimistic.
d) Dividends
Dividends are payments made by a company to its shareholders from its profits. Not all companies offer dividends, but those that do distribute them regularly as a way to reward investors.
e) Volatility
Volatility refers to the rate at which the price of a stock increases or decreases. High volatility means the price moves dramatically, while low volatility indicates more stable prices.
5. How to Start Trading Stocks
Starting in stock trading can be simple, but preparation is key. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
a) Educate Yourself
Before you begin, it’s important to learn as much as you can about stock trading. Take courses, read books, and follow stock market news. Some recommended resources include:
- “The Intelligent Investor” by Benjamin Graham
- “A Random Walk Down Wall Street” by Burton Malkiel
- Online platforms like Investopedia or Coursera for trading courses
b) Choose a Reliable Stock Trading Platform
As a beginner, you want a user-friendly trading platform with low fees and a wealth of educational resources. Some of the best platforms for beginners include:
- Robinhood: Free stock trading with a simple interface.
- E*TRADE: Great educational tools and research options.
- TD Ameritrade: Best for its extensive educational resources and paper trading options.
- Webull: Offers detailed charts and technical analysis tools.
c) Create a Trading Account
Once you’ve chosen a platform, you’ll need to open a brokerage account. You’ll be asked to provide some personal information, including your Social Security number, proof of identity, and funding method.
d) Fund Your Account
Before you start trading, you need to fund your account. You can usually transfer money from your bank to your trading account. Many brokers offer a variety of ways to deposit funds, including wire transfers, ACH transfers, and debit card payments.
e) Practice with Paper Trading
Paper trading allows you to trade with virtual money, giving you hands-on experience without the risk. This is a great way to familiarize yourself with the market, platform, and strategies before using real money.
6. Popular Trading Strategies for Beginners
Beginners should start with simple strategies before moving on to more complex approaches. Here are a few beginner-friendly stock trading strategies:
a) Buy and Hold
This is one of the simplest strategies: buy a stock and hold it for an extended period, allowing it to grow over time. Many successful investors, including Warren Buffett, favor this long-term approach.
b) Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the stock price. This method reduces the impact of volatility and allows you to buy more shares when prices are low.
c) Dividend Reinvestment
Investing in dividend-paying stocks and reinvesting the dividends to purchase more shares can lead to compounding growth over time.
d) Index Investing
Index investing involves buying stocks that make up a specific index, like the S&P 500. By purchasing an ETF or mutual fund that tracks the index, you can gain broad exposure to the stock market.
7. Tips for Managing Risk
Managing risk is a crucial aspect of stock trading. No strategy is foolproof, and losses are a part of the game. However, you can minimize them by following these risk management tips:
a) Diversify Your Portfolio
Don’t put all your money into one stock. Spread your investments across different industries and sectors to reduce risk.
b) Use Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order automatically sells a stock if it drops to a certain price, helping to limit potential losses.
c) Invest Only What You Can Afford to Lose
Never risk money you can’t afford to lose. The stock market can be volatile, and there’s always a chance of losing money.
d) Start Small
As a beginner, it’s best to start with small investments. As you gain experience and confidence, you can gradually increase your investment amounts.
8. Best Platforms for Beginners
Several online trading platforms cater to beginners by offering educational tools, easy-to-use interfaces, and low fees. Here are some top platforms to consider:
- Robinhood: Great for beginners due to its commission-free trading and easy-to-use mobile app.
- Webull: Offers more advanced tools while still being beginner-friendly.
- Fidelity: Known for its excellent customer support and educational resources.
- Charles Schwab: Ideal for beginners with its user-friendly tools and extensive educational materials.
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid
As you begin trading, it’s essential to avoid common beginner mistakes:
a) Chasing Hot Stocks
Avoid jumping on a stock just because it’s gaining attention in the media or among friends. Do your own research and invest based on your strategy.
b) Overtrading
Trading too frequently can lead to higher costs in commissions and taxes. Stick to your plan and avoid making impulsive trades.
c) Ignoring Fees
Some platforms have hidden fees, like transaction fees or inactivity fees. Make sure you’re aware of all the costs associated with your trades.
d) Letting Emotions Drive Decisions
Fear and greed are two of the biggest enemies of successful traders. Stick to your strategy, and don’t let emotions dictate your trades.
10. Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Stock trading can be a rewarding way to grow your wealth, but it’s important to start with the right mindset and a solid plan. As a beginner, focus on educating yourself, practicing with paper trading, and managing your risk. Be patient, and understand that becoming a successful trader takes time and experience.
By following the guidelines in this beginner’s guide, you’ll be well on your way to building a foundation for successful stock trading. Remember, trading is not a get-rich-quick scheme. With persistence, discipline, and ongoing learning, you can master the art of stock trading and achieve your financial goals.