Forex trading has gained immense popularity in recent years, leading to an increase in the number of forex brokers available to traders. Selecting the right broker is a crucial step in your trading journey, as it can significantly affect your trading experience and profitability. Two of the most common types of forex brokers are ECN (Electronic Communication Network) and Market Maker brokers. This article will delve into the differences between these two broker types, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the best one for your trading needs.
1. Understanding Forex Brokers
What is a Forex Broker?
A forex broker acts as an intermediary between retail traders and the interbank forex market. They provide a trading platform for individuals to buy and sell currency pairs. Forex brokers can offer different trading conditions, spreads, commissions, and order execution methods, which can significantly influence a trader’s experience.
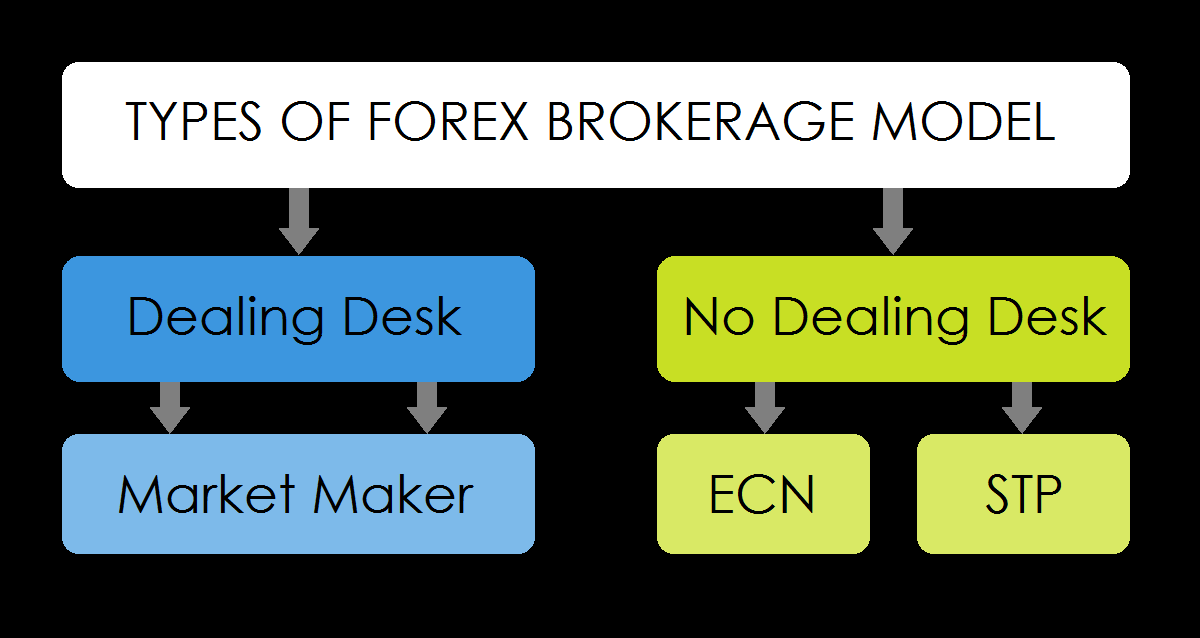
Types of Forex Brokers
Forex brokers can generally be classified into two main categories:
- Market Maker (MM): Market makers provide liquidity to the market by quoting both buy and sell prices for currency pairs. They profit from the spread, which is the difference between the bid and ask price.
- ECN (Electronic Communication Network): ECN brokers connect traders directly to the interbank forex market, allowing them to trade with other market participants. They typically charge a commission or a small markup on the spread.
2. Overview of ECN Brokers
How ECN Brokers Work
ECN brokers facilitate direct trading between clients and liquidity providers (such as banks and financial institutions). When a trader places an order, the broker matches the order with the best available prices from multiple liquidity providers, resulting in a more competitive pricing environment.
Key Features of ECN Brokers
- Direct Market Access: ECN brokers provide traders with direct access to the interbank market, allowing for faster execution of orders.
- Variable Spreads: Spreads can vary based on market conditions and liquidity, often leading to tighter spreads during high volatility.
- No Dealing Desk: ECN brokers do not have a dealing desk, which means they do not take the other side of the trade. This eliminates potential conflicts of interest.
Advantages of ECN Brokers
- Transparency: ECN brokers offer a transparent trading environment where traders can see real-time market prices and liquidity.
- Tight Spreads: Due to the competition among liquidity providers, ECN brokers can offer tighter spreads compared to market makers.
- Faster Execution: Orders are executed quickly as they are sent directly to the interbank market, reducing slippage during volatile market conditions.
- Diverse Trading Options: ECN brokers often allow for a wider range of trading strategies, including scalping and automated trading.
Disadvantages of ECN Brokers
- Commission Fees: ECN brokers typically charge commissions on trades, which can add to trading costs.
- Variable Spreads: While spreads may be tighter during active market conditions, they can widen significantly during low liquidity periods.
- Minimum Deposit Requirements: ECN brokers may have higher minimum deposit requirements compared to market makers.
3. Overview of Market Maker Brokers
How Market Maker Brokers Work
Market maker brokers create a market for traders by offering buy and sell prices for currency pairs. They take the other side of trades, meaning they may profit from losing trades while providing liquidity to winning trades. Market makers often hedge their exposure to manage risk.
Key Features of Market Maker Brokers
- Fixed Spreads: Market makers usually offer fixed spreads, which remain constant regardless of market conditions.
- Dealing Desk: Market makers operate a dealing desk to manage orders and quotes, which may create potential conflicts of interest.
- In-house Liquidity: Market makers can provide liquidity by holding positions internally, ensuring that traders can execute orders without significant delays.
Advantages of Market Maker Brokers
- Fixed Spreads: Traders can benefit from predictable trading costs, as spreads remain constant.
- Lower Minimum Deposits: Market makers typically have lower minimum deposit requirements, making them more accessible for beginners.
- Ease of Use: The straightforward pricing structure can be easier for novice traders to understand.
Disadvantages of Market Maker Brokers
- Conflict of Interest: Market makers may have a conflict of interest when taking the opposite side of trades, potentially leading to less favorable pricing for traders.
- Wider Spreads in Low Liquidity: Although spreads are fixed, they can be wider during low liquidity periods compared to ECN brokers.
- Slower Execution: Orders may be executed at different prices due to the dealing desk model, especially during periods of high volatility.
4. Key Differences Between ECN and Market Maker Brokers
| Feature | ECN Brokers | Market Maker Brokers |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Model | Direct market access | Dealing desk model |
| Spreads | Variable, typically tighter | Fixed, predictable spreads |
| Commission Structure | May charge commissions | Typically no commissions, profit from spread |
| Liquidity | Access to multiple liquidity providers | Internal liquidity |
| Order Execution | Faster, less slippage | May experience slippage |
| Conflict of Interest | No conflict of interest | Potential conflict due to internal pricing |
| Minimum Deposit | Higher minimum deposits | Lower minimum deposits |
| Trading Strategies | Supports scalping and algorithmic trading | More suitable for long-term strategies |
5. Choosing the Right Broker for Your Trading Style
Factors to Consider
- Trading Style: Your trading style plays a significant role in selecting the right broker. If you prefer scalping or high-frequency trading, an ECN broker may be more suitable. If you are a beginner or prefer a long-term approach, a market maker may be more appropriate.
- Cost of Trading: Consider the overall cost of trading, including spreads and commissions. While ECN brokers may offer tighter spreads, the commissions can add up, especially for frequent traders.
- Trading Platform: Assess the trading platforms offered by brokers. Some brokers provide advanced charting tools and features that may benefit your trading strategy.
- Regulation: Choose a regulated broker to ensure a level of protection for your funds. Research the broker’s regulatory status and reputation in the industry.
- Customer Support: Good customer support can make a significant difference in your trading experience. Ensure that the broker offers reliable support channels, such as live chat, email, or phone.
Personal Preferences
Ultimately, your preferences and trading goals should guide your choice of broker. Consider testing both types of brokers using demo accounts to see which aligns best with your trading style.
6. Conclusion
Choosing the right forex broker is a critical decision that can impact your trading success. Both ECN and market maker brokers offer unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different types of traders.
ECN brokers provide direct access to the interbank market, tighter spreads, and faster execution, making them ideal for active traders and scalpers. On the other hand, market makers offer fixed spreads, lower minimum deposits, and a straightforward pricing structure, appealing to beginners and long-term investors.
As a trader, it is essential to assess your trading style, cost considerations, and personal preferences when selecting a broker. Conduct thorough research, read reviews, and, if possible, test both types of brokers through demo accounts. With the right broker, you can enhance your trading experience and increase your chances of success in the dynamic forex market.