Scalping in Forex trading is a popular strategy among traders looking to capitalize on small price movements. This approach involves making multiple trades throughout the day to capture tiny price changes, which can add up to significant profits over time. While scalping can be a lucrative trading style, it requires a solid understanding of market mechanics, effective risk management, and a disciplined mindset.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of scalping in Forex, the necessary tools and techniques, effective strategies, risk management practices, and common challenges traders face. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of scalping and how to implement it successfully in your trading.
Table of Contents
- What is Scalping?
- 1.1. Definition of Scalping
- 1.2. Characteristics of Scalping
- 1.3. Why Traders Choose Scalping
- The Basics of Scalping in Forex
- 2.1. Understanding the Forex Market
- 2.2. Timeframes and Scalping
- 2.3. Scalping vs. Other Trading Styles
- Tools and Techniques for Scalping
- 3.1. Trading Platforms and Software
- 3.2. Key Indicators for Scalping
- 3.3. Chart Patterns and Scalping
- Effective Scalping Strategies
- 4.1. Market Making
- 4.2. Trend Following
- 4.3. Range Trading
- 4.4. News-Based Scalping
- Risk Management in Scalping
- 5.1. Importance of Risk Management
- 5.2. Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
- 5.3. Position Sizing for Scalpers
- Challenges and Common Mistakes in Scalping
- 6.1. Emotional Challenges
- 6.2. Overtrading
- 6.3. Ignoring Market Conditions
- Developing a Scalping Plan
- 7.1. Setting Goals and Objectives
- 7.2. Backtesting and Analyzing Strategies
- 7.3. Continuous Learning and Improvement
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Scalping?
1.1. Definition of Scalping
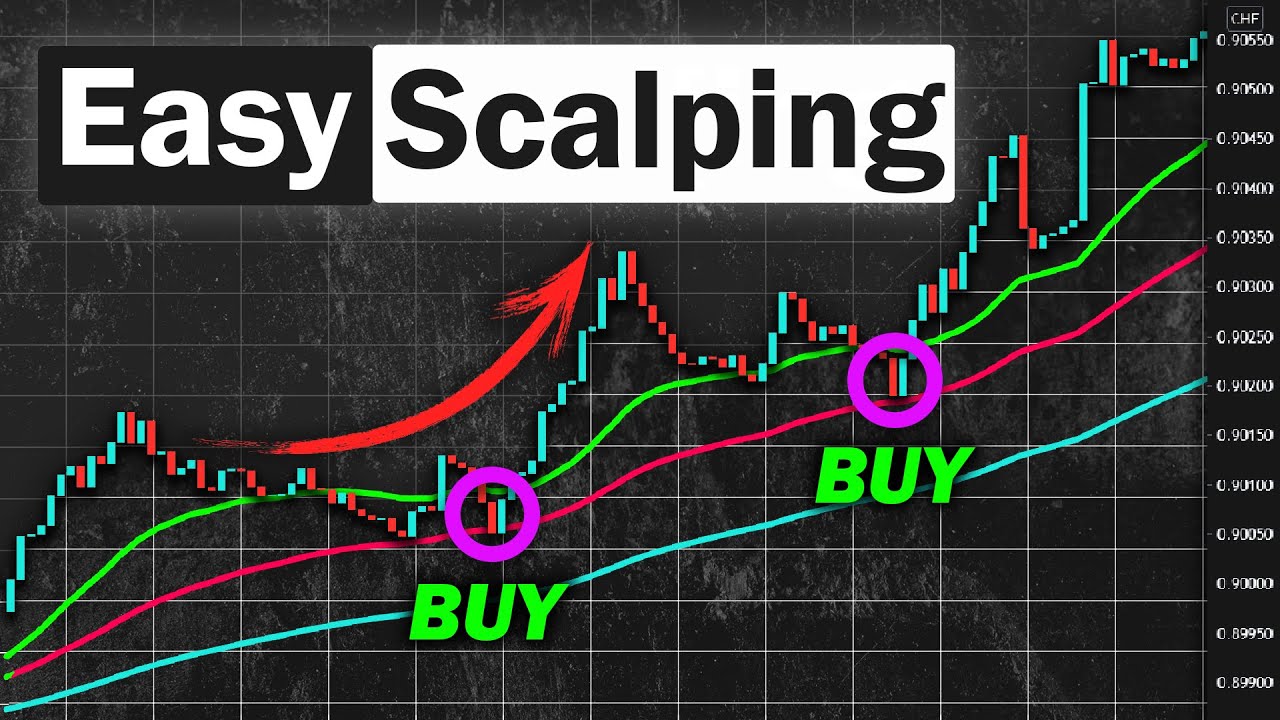
Scalping is a trading strategy that aims to profit from small price movements by executing numerous trades within a short period. Scalpers typically hold positions for seconds to minutes, making quick trades to capitalize on small price fluctuations. The goal is to accumulate multiple small profits that can result in a substantial overall gain.
1.2. Characteristics of Scalping
Several key characteristics define scalping as a trading strategy:
- Short Holding Period: Scalpers hold positions for very brief periods, often just a few seconds to a few minutes.
- High Trade Frequency: Scalpers execute a large number of trades each day, sometimes making dozens or even hundreds of trades in a single session.
- Small Profit Targets: Scalpers aim for small profit margins, typically ranging from 2 to 10 pips per trade.
- Use of Leverage: Many scalpers utilize leverage to amplify their returns, allowing them to take larger positions relative to their capital.
1.3. Why Traders Choose Scalping
Traders may choose scalping for several reasons:
- Quick Profits: Scalping allows traders to realize profits quickly, making it appealing for those who prefer a fast-paced trading environment.
- Less Exposure to Market Risk: Since positions are held for short periods, scalpers are less exposed to adverse market movements compared to longer-term traders.
- Consistent Income: For some traders, scalping can provide a consistent stream of income, as multiple trades can be executed daily.
2. The Basics of Scalping in Forex
Before diving into scalping strategies, it’s important to understand the fundamentals of the Forex market and how they relate to scalping.
2.1. Understanding the Forex Market
The Forex market is the largest financial market in the world, where currencies are traded in pairs. Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY, tend to have the highest liquidity and volatility, making them suitable for scalping.
Key aspects of the Forex market that scalpers should understand include:
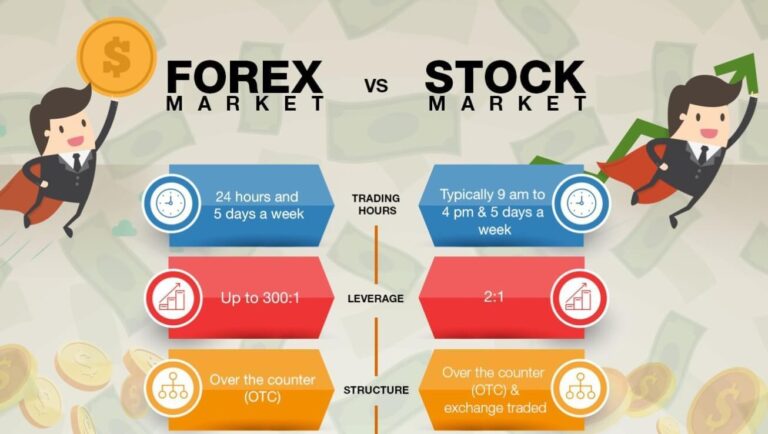
- Market Hours: The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing scalpers to trade at various times depending on market activity and liquidity.
- Liquidity and Spreads: High liquidity in major currency pairs typically results in lower spreads (the difference between the bid and ask price), which is advantageous for scalpers looking to minimize trading costs.
- Market Volatility: Scalpers thrive in volatile market conditions, where rapid price movements can create more opportunities for profit.
2.2. Timeframes and Scalping
Scalpers typically use shorter timeframes to identify entry and exit points. Commonly used timeframes for scalping include:
- 1-Minute Charts: Provides the most granular view of price movements, allowing scalpers to make quick decisions based on rapid fluctuations.
- 5-Minute Charts: Offers a slightly broader perspective while still allowing for quick trades.
- Tick Charts: Displays price movements based on a specific number of trades rather than time, enabling scalpers to analyze price action without the influence of time.
2.3. Scalping vs. Other Trading Styles
Scalping differs from other trading styles, such as day trading, swing trading, and position trading:
- Day Trading: Day traders hold positions for hours and close them by the end of the trading day. While day trading shares some similarities with scalping, it generally involves larger price targets and longer holding periods.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders aim to capture price movements over several days or weeks, often using technical analysis and chart patterns to identify entry and exit points.
- Position Trading: Position traders hold positions for extended periods, from weeks to months, relying on fundamental analysis and long-term trends.
Scalping is distinct in its focus on short-term price movements and high trade frequency.
3. Tools and Techniques for Scalping
To succeed in scalping, traders must utilize the right tools and techniques. Here are some essential components for effective scalping:
3.1. Trading Platforms and Software
Choosing the right trading platform is critical for scalpers. Key features to look for include:
- Low Latency: Fast execution speeds are essential for scalping, as delays can lead to missed opportunities.
- User-Friendly Interface: A platform that is easy to navigate allows scalpers to make quick decisions without confusion.
- Advanced Charting Tools: Scalpers should have access to advanced charting tools and indicators to analyze price action effectively.
Popular trading platforms for scalping include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and various broker-specific platforms.
3.2. Key Indicators for Scalping
Several technical indicators can assist scalpers in making informed trading decisions:
- Moving Averages: Moving averages, such as the 50-period and 200-period moving averages, can help identify trends and potential reversal points.
- Bollinger Bands: This volatility indicator can signal overbought or oversold conditions, providing potential entry and exit points.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI helps identify overbought or oversold conditions, assisting scalpers in determining potential price reversals.
- Stochastic Oscillator: This momentum indicator can provide insights into potential entry points by identifying overbought or oversold conditions.
3.3. Chart Patterns and Scalping
Scalpers often use chart patterns to identify potential trade setups. Key patterns to watch for include:
- Triangles: Ascending and descending triangles can signal potential breakouts, providing scalping opportunities.
- Flags and Pennants: These continuation patterns can indicate brief pauses in price movements before the trend resumes, making them suitable for scalpers.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Identifying key support and resistance levels can help scalpers determine entry and exit points.
4. Effective Scalping Strategies
Several strategies can be employed in scalping, each with its unique approach. Here are some effective scalping strategies:
4.1. Market Making
Market-making involves placing buy and sell orders at different price levels to capture the spread between them. Market makers provide liquidity to the market by simultaneously offering to buy and sell a currency pair. Key aspects of market-making include:
- Bid-Ask Spread: Scalpers profit from the difference between the buying (bid) and selling (ask) prices.
- Limit Orders: Placing limit orders at various price levels can allow scalpers to capture small price movements without constantly monitoring the market.
4.2. Trend Following
Trend-following scalping focuses on identifying and trading in the direction of the prevailing trend. To implement this strategy:
- Identify the Trend: Use moving averages or trendlines to determine the overall direction of the market.
- Enter on Pullbacks: Look for pullbacks in the direction of the trend as potential entry points.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders to manage risk in case the trend reverses.
- Take Profit: Aim for small profit targets that align with the overall trend.
4.3. Range Trading
Range trading involves identifying key support and resistance levels and trading within the established range. To implement this strategy:
- Identify Range Boundaries: Determine the upper and lower boundaries of the price range.
- Buy at Support: Enter long positions near the support level and exit near the resistance level.
- Sell at Resistance: Enter short positions near the resistance level and exit near the support level.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders just outside the range to manage risk.
4.4. News-Based Scalping
News events can create significant volatility in the Forex market, providing scalping opportunities. To implement news-based scalping:
- Monitor Economic Calendar: Stay informed about upcoming economic releases and news events that can impact currency prices.
- Trade the Reaction: Enter trades immediately after the news release, capitalizing on rapid price movements.
- Use Tight Stop-Loss Orders: Due to the potential for increased volatility, use tight stop-loss orders to manage risk effectively.
5. Risk Management in Scalping
Effective risk management is crucial for successful scalping. Here are some key considerations:
5.1. Importance of Risk Management
Risk management helps traders protect their capital and minimize losses. Scalping can be highly risky due to the rapid pace of trades, making effective risk management essential.
5.2. Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Establishing clear stop-loss and take-profit levels is critical for managing risk in scalping:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders at predetermined levels based on technical analysis or a percentage of your account balance to limit potential losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: Set take-profit levels to secure gains and exit trades automatically when a specific profit target is reached.
5.3. Position Sizing for Scalpers
Proper position sizing is essential for managing risk in scalping. Consider the following guidelines:
- Risk Percentage: Risk only a small percentage of your trading capital (e.g., 1-2%) on any single trade to avoid significant losses.
- Calculate Position Size: Use position size calculators to determine the appropriate lot size based on your risk tolerance and stop-loss distance.
6. Challenges and Common Mistakes in Scalping
While scalping can be lucrative, traders often face challenges and make common mistakes. Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
6.1. Emotional Challenges
Scalping can be emotionally taxing due to the rapid pace of trading. Traders may experience fear of missing out (FOMO), anxiety, or impulsive decision-making. To combat these emotions:
- Stick to Your Plan: Follow your trading plan and avoid making impulsive trades based on emotions.
- Practice Discipline: Maintain discipline in executing trades and adhering to your risk management strategy.
6.2. Overtrading
Overtrading is a common mistake among scalpers, driven by the desire to capture every opportunity. To avoid overtrading:
- Set Limits: Establish daily or weekly limits on the number of trades you will execute.
- Focus on Quality: Prioritize high-quality setups over quantity, as chasing trades can lead to increased transaction costs and losses.
6.3. Ignoring Market Conditions
Scalpers should always consider overall market conditions. Trading against the prevailing trend or during low liquidity periods can increase the risk of losses. Stay informed about economic events, news releases, and market sentiment to make informed trading decisions.
7. Developing a Scalping Plan
To succeed in scalping, it’s essential to develop a well-defined trading plan. Here’s how to create an effective scalping plan:
7.1. Setting Goals and Objectives
Establish clear trading goals and objectives, such as:
- Profit Targets: Define your desired profit target for each trading session or week.
- Risk Tolerance: Determine the amount of risk you are willing to take on each trade.
- Time Commitment: Decide how much time you can dedicate to scalping each day or week.
7.2. Backtesting and Analyzing Strategies
Before implementing a scalping strategy in live trading, backtest it using historical data. Analyze past performance to identify strengths and weaknesses, and make adjustments as needed.
7.3. Continuous Learning and Improvement
Scalping requires ongoing education and improvement. Stay informed about market developments, new strategies, and trading psychology to enhance your skills. Consider joining trading communities or forums to share experiences and learn from others.
8. Conclusion
Scalping in Forex trading can be a rewarding strategy for traders who thrive in fast-paced environments. By understanding the fundamentals of scalping, utilizing the right tools and techniques, implementing effective strategies, and practicing sound risk management, traders can capitalize on small price movements for potential profits.
While scalping presents unique challenges, traders who develop a well-defined trading plan, maintain discipline, and continuously improve their skills can succeed in this dynamic trading style. Whether you are a novice or an experienced trader, scalping offers opportunities for profit and excitement in the Forex market.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is scalping suitable for beginners?
Yes, scalping can be suitable for beginners, but it requires a solid understanding of market mechanics, effective risk management, and the ability to make quick decisions. Beginners should practice scalping on demo accounts before risking real capital.
2. What is the best timeframe for scalping in Forex?
Scalpers typically use shorter timeframes, such as 1-minute or 5-minute charts, to identify quick trading opportunities.
3. How much capital do I need to start scalping?
The amount of capital needed to start scalping varies, but traders should have enough funds to cover spreads, commissions, and potential losses. A minimum of $1,000 to $5,000 is often recommended, but it’s essential to assess individual risk tolerance.
4. Can I scalp in a volatile market?
Yes, volatile markets can present excellent opportunities for scalpers, as rapid price movements create more potential for profit. However, increased volatility also comes with heightened risk, so effective risk management is essential.
5. How do I choose a Forex broker for scalping?
When choosing a broker for scalping, look for low spreads, fast execution speeds, and a user-friendly trading platform. Additionally, ensure the broker allows scalping and does not impose restrictions on high-frequency trading.