Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, involves buying and selling currencies to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. While it can be an exciting and potentially profitable endeavor, beginners often find it challenging to navigate the complexities of the forex market. To help new traders, this article outlines ten effective forex trading strategies that can lay the foundation for a successful trading career.
1. Understanding Forex Basics
Before diving into trading strategies, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental concepts of forex trading.
What is Forex Trading?
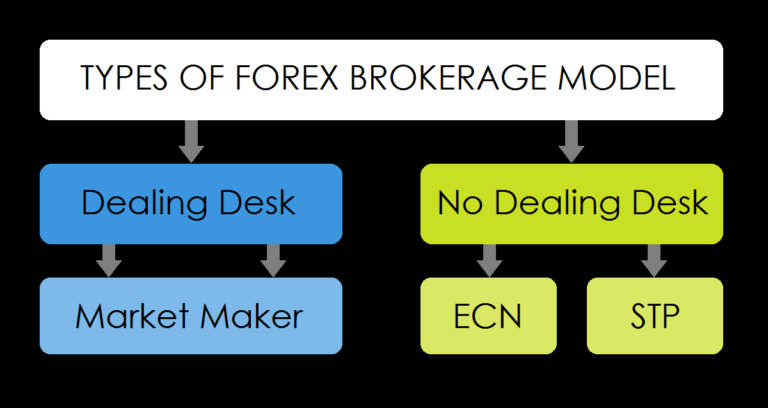
Forex trading involves the exchange of one currency for another in the foreign exchange market. Currency pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY, represent the exchange rate between two currencies. Traders speculate on the future movements of these pairs to generate profits.
Key Terms to Know
- Pips: The smallest price movement in a currency pair, often the fourth decimal place.
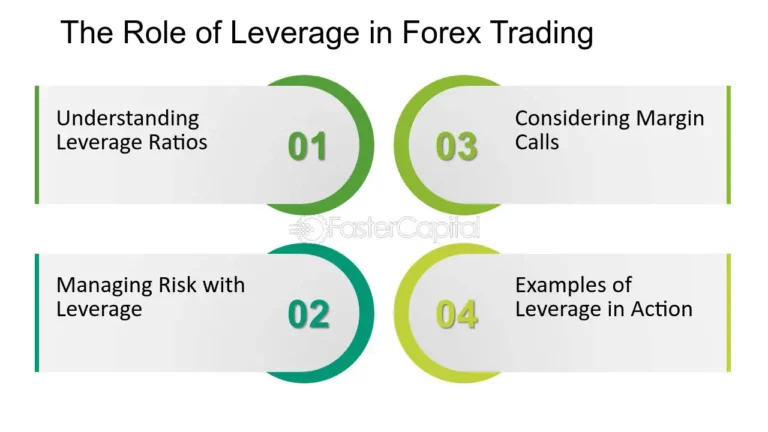
- Leverage: The ability to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital, which can amplify profits but also increases risk.
- Spread: The difference between the bid (selling) and ask (buying) price of a currency pair.
- Lot Size: The volume of currency units traded, with standard lots representing 100,000 units.
2. Fundamental Analysis
What is Fundamental Analysis?
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating economic indicators, news events, and geopolitical factors that can influence currency values. By understanding the underlying economic conditions, traders can make informed decisions about which currencies to buy or sell.
Key Economic Indicators to Monitor
- Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates, which influence currency values. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign capital, leading to currency appreciation.
- Inflation: Inflation levels can affect purchasing power and influence central bank policies. Monitoring Consumer Price Index (CPI) data is essential.
- Employment Data: Non-farm payrolls (NFP) and unemployment rates provide insights into economic health and labor market conditions.
- GDP Growth: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures economic activity and growth, affecting currency strength.
Fundamental Analysis Strategy
- Economic Calendar: Use an economic calendar to track upcoming economic releases and news events that could impact currency pairs.
- News Sentiment: Assess market sentiment around major news events, as positive or negative news can lead to volatility.
3. Technical Analysis
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis involves studying historical price movements and chart patterns to forecast future price action. Traders use various tools and indicators to analyze price charts and make trading decisions.
Key Chart Types
- Line Charts: Simple charts that connect closing prices over a specified period.
- Bar Charts: Display opening, closing, high, and low prices for a specific time frame.
- Candlestick Charts: Popular charts that provide more detail about price movements, showing open, close, high, and low prices in a visually appealing format.
Key Technical Indicators
- Moving Averages: Help smooth out price data to identify trends over time. Commonly used moving averages include the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): A momentum oscillator that indicates overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI above 70 suggests overbought conditions, while an RSI below 30 indicates oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Measure market volatility and identify potential price reversals. Prices touching the upper band may indicate overbought conditions, while prices touching the lower band may suggest oversold conditions.
4. Scalping Strategy
What is Scalping?
Scalping is a short-term trading strategy that aims to profit from small price movements by making numerous trades throughout the day. Scalpers typically hold positions for a few seconds to a few minutes.
Key Aspects of Scalping
- Time Frame: Scalpers often use 1-minute or 5-minute charts for quick decision-making.
- Quick Execution: Speed is crucial in scalping. Traders need to execute trades rapidly to capture small profits.
- Tight Spreads: Choose currency pairs with tight spreads to minimize trading costs.
Scalping Strategy Steps
- Choose a Currency Pair: Select a currency pair with high liquidity and volatility, such as EUR/USD or GBP/USD.
- Set Up Technical Indicators: Use indicators like moving averages and RSI to identify entry and exit points.
- Manage Risk: Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade.
5. Day Trading Strategy
What is Day Trading?
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day. Day traders seek to profit from intraday price movements and typically avoid holding positions overnight to mitigate risk.
Key Aspects of Day Trading
- Time Frame: Day traders often use 15-minute, 30-minute, or 1-hour charts to identify trading opportunities.
- Volatility: Look for currency pairs with significant price movements throughout the day to capitalize on fluctuations.
- Risk Management: Implement strict risk management strategies to protect your capital.
Day Trading Strategy Steps
- Select Currency Pairs: Focus on a few major currency pairs to gain familiarity with their price behavior.
- Analyze Price Movements: Use technical analysis to identify support and resistance levels, trend lines, and patterns.
- Set Profit Targets and Stop Losses: Determine realistic profit targets and place stop-loss orders to protect against adverse price movements.
6. Swing Trading Strategy
What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a medium-term trading strategy that aims to capture price swings over several days or weeks. Swing traders typically analyze price charts and fundamental factors to make informed decisions.
Key Aspects of Swing Trading
- Time Frame: Swing traders often use daily or 4-hour charts to identify potential price swings.
- Holding Period: Positions are held for several days to capture significant price movements.
- Technical and Fundamental Analysis: Swing traders may use both technical and fundamental analysis to inform their decisions.
Swing Trading Strategy Steps
- Identify Trends: Use moving averages and trend lines to identify the direction of the market.
- Look for Reversals: Look for potential reversal points using candlestick patterns or support and resistance levels.
- Set Entry and Exit Points: Determine entry and exit points based on technical analysis and market sentiment.
7. Position Trading Strategy
What is Position Trading?
Position trading is a long-term trading strategy that involves holding positions for weeks, months, or even years. Position traders focus on the long-term trends in the forex market rather than short-term fluctuations.
Key Aspects of Position Trading
- Time Frame: Position traders typically use weekly or monthly charts for analysis.
- Fundamental Analysis: Emphasis is placed on fundamental factors that can affect currency values over the long term.
- Less Frequent Trading: Position traders make fewer trades compared to scalpers or day traders.
Position Trading Strategy Steps
- Analyze Economic Fundamentals: Research economic indicators, geopolitical events, and central bank policies that may affect currency pairs.
- Identify Long-Term Trends: Use moving averages and trend lines to identify potential long-term trends.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Protect against adverse price movements by setting stop-loss orders at strategic levels.
8. Risk Management Strategies
Importance of Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success in forex trading. Proper risk management helps protect your capital and minimizes potential losses.
Key Risk Management Techniques
- Position Sizing: Determine the appropriate position size based on your account balance and risk tolerance. A common guideline is to risk no more than 1-2% of your capital on a single trade.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Always set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade. This ensures that you exit a losing trade before it significantly impacts your account.
- Take-Profit Orders: Use take-profit orders to secure profits once your target price is reached, allowing for disciplined exits.
Risk Management Strategy Steps
- Determine Risk Tolerance: Assess how much risk you are willing to take on each trade and adjust your position size accordingly.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Establish clear stop-loss and take-profit levels before entering a trade.
- Regularly Review Performance: Continuously assess your trading performance and adjust your risk management strategies as needed.
9. The Importance of a Trading Plan
What is a Trading Plan?
A trading plan is a comprehensive outline that details your trading strategies, risk management rules, and goals. Having a trading plan helps maintain discipline and consistency in your trading approach.
Key Components of a Trading Plan
- Trading Goals: Define your short-term and long-term trading goals.
- Trading Strategies: Outline the specific trading strategies you will use, including entry and exit criteria.
- Risk Management Rules: Specify your risk tolerance, position sizing, and stop-loss and take-profit strategies.
- Performance Evaluation: Plan how you will review and evaluate your trading performance regularly.
Trading Plan Steps
- Write Down Your Plan: Document your trading goals, strategies, and risk management rules in a clear and concise manner.
- Stick to Your Plan: Follow your trading plan consistently, avoiding impulsive decisions based on emotions.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review your trading plan and make adjustments as necessary based on your performance and changing market conditions.
10. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Importance of Ongoing Education
The forex market is constantly evolving, and staying informed about market trends, economic events, and new trading strategies is crucial for success. Continuous learning helps you adapt to changing conditions and improve your trading skills.
Key Learning Resources
- Books: Read books on forex trading, technical analysis, and market psychology to deepen your understanding.
- Online Courses: Enroll in online courses or webinars that cover various aspects of forex trading.
- Trading Communities: Join trading forums or communities to exchange ideas and learn from experienced traders.
Learning and Adaptation Steps
- Set Aside Time for Learning: Dedicate time each week to study and improve your trading knowledge.
- Practice with a Demo Account: Use a demo trading account to practice your strategies without risking real money.
- Stay Updated on Market News: Follow financial news and economic updates to stay informed about factors influencing the forex market.
Conclusion
Forex trading offers exciting opportunities for beginners to profit from currency fluctuations. However, it also comes with inherent risks that require careful consideration and planning. By understanding the basics of forex trading and implementing effective strategies, new traders can navigate the market with confidence.
The ten strategies outlined in this guide provide a solid foundation for beginners to build upon. From fundamental and technical analysis to risk management and the importance of a trading plan, each aspect plays a crucial role in achieving success in the forex market. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying competitive and making informed trading decisions.
As you embark on your forex trading journey, remember that patience, discipline, and a commitment to learning are essential ingredients for success. With time and practice, you can develop the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in this dynamic market. Happy trading!