The DXY, or the US Dollar Index, is a crucial benchmark for traders, investors, and economists alike. It measures the value of the United States dollar relative to a basket of foreign currencies, providing insight into the dollar’s strength in the global market. This article delves into the DXY, exploring its components, significance, impact on forex markets, and strategies for trading it effectively.
Table of Contents
- What is the DXY US Dollar Index?
- Definition and Purpose
- Historical Background
- Components of the DXY
- Currency Weights
- Key Trading Partners
- How the DXY is Calculated
- The Calculation Formula
- Interpretation of DXY Movements
- The Significance of the DXY
- Economic Indicators
- Market Sentiment
- Factors Influencing the DXY
- Interest Rates
- Inflation
- Economic Data Releases
- Geopolitical Events
- Impact of the DXY on Forex Markets
- Correlation with Currency Pairs
- Trading Strategies Involving the DXY
- Trading the DXY
- Instruments for Trading
- Risk Management Techniques
- Conclusion and Future Outlook for the DXY
1. What is the DXY US Dollar Index?
Definition and Purpose
The DXY US Dollar Index measures the strength of the US dollar against a basket of six major currencies: Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Canadian Dollar (CAD), Swedish Krona (SEK), and Swiss Franc (CHF). The index is designed to provide a comprehensive view of the dollar’s performance in the global market.
Historical Background
The DXY was introduced in 1973 after the Bretton Woods Agreement, which established fixed exchange rates for currencies. The index has evolved over the years but remains a critical tool for assessing the dollar’s value against other currencies. It serves as a benchmark for international trade and investment decisions, reflecting economic trends and geopolitical developments.
2. Components of the DXY
Currency Weights
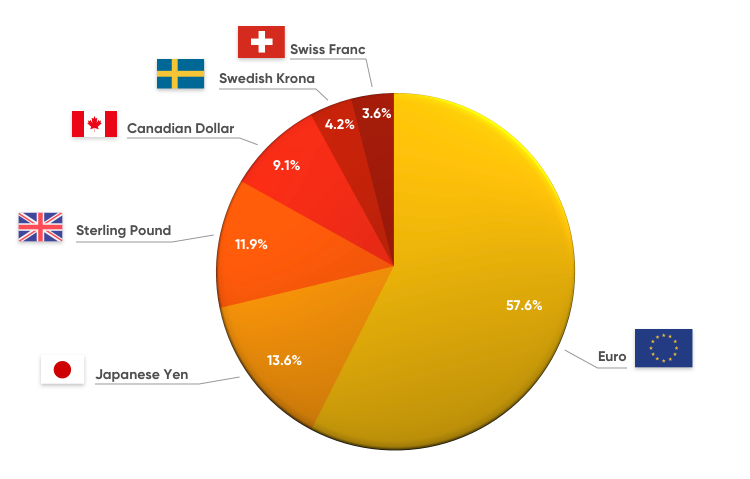
The DXY is not a simple average of the currencies it tracks; rather, it uses a weighted geometric mean. The weights assigned to each currency reflect their relative importance in international trade. Here’s a breakdown of the weights as of 2023:
- Euro (EUR): 57.6%
- Japanese Yen (JPY): 13.6%
- British Pound (GBP): 11.9%
- Canadian Dollar (CAD): 9.1%
- Swedish Krona (SEK): 4.2%
- Swiss Franc (CHF): 3.6%
Key Trading Partners
The currencies included in the DXY represent some of the United States’ largest trading partners. The Euro, for instance, accounts for over half of the index, highlighting the significance of the Eurozone in the global economy. Understanding these components helps traders anticipate how shifts in economic conditions will impact the DXY.
3. How the DXY is Calculated
The Calculation Formula
The DXY is calculated using the following formula:
DXY=50.14348112×(EUR−0.576)×(JPY0.136)×(GBP0.119)×(CAD0.091)×(SEK0.042)×(CHF0.036)DXY = 50.14348112 \times (EUR^{-0.576}) \times (JPY^{0.136}) \times (GBP^{0.119}) \times (CAD^{0.091}) \times (SEK^{0.042}) \times (CHF^{0.036})
The values of each currency are derived from the current exchange rates, and their respective weights are applied to reflect their influence on the overall index.
Interpretation of DXY Movements
An increase in the DXY indicates a strengthening of the US dollar relative to the basket of currencies, while a decrease signifies a weakening dollar. Traders and investors closely monitor the DXY for insights into economic health and market trends.
4. The Significance of the DXY
Economic Indicators
The DXY serves as a leading economic indicator. A strong dollar can signal confidence in the US economy, while a weak dollar may indicate economic challenges. Businesses and policymakers use the index to make informed decisions regarding investments, pricing strategies, and monetary policy.
Market Sentiment
The DXY reflects overall market sentiment towards the US dollar. A rising index may indicate a flight to safety among investors during times of uncertainty, while a falling index may suggest risk appetite and confidence in alternative assets.
5. Factors Influencing the DXY
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by the Federal Reserve have a significant impact on the DXY. Higher interest rates typically strengthen the dollar, as they offer better returns on investments denominated in dollars. Conversely, lower interest rates may weaken the dollar.
Inflation
Inflation rates can erode the purchasing power of a currency, impacting the DXY. Higher inflation in the US relative to other countries may lead to a depreciation of the dollar. Monitoring inflation trends is crucial for understanding potential DXY movements.
Economic Data Releases
Key economic indicators, such as GDP growth, employment figures, and consumer spending, influence the DXY. Strong economic data typically supports a stronger dollar, while weak data may lead to declines.
Geopolitical Events
Global events, such as conflicts, trade disputes, and elections, can create uncertainty and volatility in the forex market. The DXY often reacts to geopolitical developments, with investors seeking safe-haven assets like the dollar during turbulent times.
6. Impact of the DXY on Forex Markets
Correlation with Currency Pairs
The DXY has a significant impact on various currency pairs, particularly those involving the US dollar. A strong DXY often correlates with falling prices in currency pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD, while a weak DXY can result in rising prices for these pairs.
Trading Strategies Involving the DXY
Traders often use the DXY to inform their trading strategies. For instance:
- Trend Following: If the DXY shows a consistent upward trend, traders may take long positions in USD-denominated assets.
- Mean Reversion: Some traders may look for opportunities to sell USD when the DXY is significantly overbought or oversold, betting on a return to the mean.
- Hedging: Traders can use the DXY to hedge positions in other currencies or commodities, such as gold, which often inversely correlates with the dollar.
7. Trading the DXY
Instruments for Trading
Traders have several options for trading the DXY:
- Futures Contracts: Futures contracts on the DXY are available on exchanges, allowing traders to speculate on future movements in the index.
- ETFs: Exchange-Traded Funds that track the DXY provide an accessible way to gain exposure to the index without directly trading futures.
- Forex Pairs: Traders can also trade specific currency pairs that are influenced by the DXY, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY.
Risk Management Techniques
Effective risk management is crucial when trading the DXY. Some techniques include:
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Protect your capital by setting stop-loss orders at predetermined levels.
- Position Sizing: Adjust your position size based on your risk tolerance and the volatility of the DXY.
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different asset classes to mitigate risk.
8. Conclusion and Future Outlook for the DXY
The DXY US Dollar Index serves as a vital tool for understanding the dynamics of the global forex market. Its ability to reflect the strength of the US dollar against a basket of currencies makes it an essential benchmark for traders and investors.
As we look to the future, several factors will continue to influence the DXY, including interest rates, inflation trends, and geopolitical developments. Understanding these factors and their implications for the DXY can provide traders with valuable insights and opportunities.
For those interested in trading the DXY, staying informed about economic indicators, market sentiment, and global events will be key to successful trading strategies. By utilizing effective risk management techniques and understanding the complexities of the index, traders can navigate the dynamic forex landscape with confidence.
In conclusion, the DXY is not just a number; it represents the economic health of the United States and its position in the global economy. By analyzing the DXY and its components, traders can make informed decisions, ultimately leading to more successful trading outcomes. Happy trading!